Designing products without usability testing is like throwing darts in the dark.
For enterprise applications and healthcare software, usability testing emerges as a guiding light toward user satisfaction and efficiency.
It’s not just about making things work; it’s about making them work for the people who use them.
This practice extends beyond the boundaries of conventional design, focusing on how actual users interact with and experience a product.
With design taking center stage in business strategies, the emphasis shifts from solely meeting business objectives to aligning with user needs.
It’s a process that ensures products are not only aligned with business goals but are also intuitive and user-centric, significantly impacting the product’s success and the business’s profitability.
In this usability testing guide, we aim to demystify usability testing, outlining its importance, definitions, and broad scope, specifically in the realms of enterprise application testing and usability in healthcare.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a technique used to evaluate a product by testing it with representative users. Selecting the right test participants is crucial to ensure the feedback is relevant and actionable. This process involves observing users as they interact with the product, aiming to identify any usability issues and gather qualitative data about the users’ experiences.
For example, a company might conduct usability testing on a new mobile app by asking users to complete specific tasks while observing how easily and efficiently they can navigate the app. This real-world feedback is crucial for refining the app’s design and functionality, ensuring it meets user needs and expectations effectively.
The Need For Enterprise Usability Testing
Enterprise systems have traditionally prioritized organizational needs over user satisfaction. However, the importance of enterprise user experience (UX) in enterprise systems has gained recognition in recent times. A well-executed UX methodology can lead to increased productivity, faster processes, seamless data portability, a focus on innovation, and a motivated workforce.
eUX is known to help draw the right balance between the expectations of the business and the needs of the users it helps them maximize their productivity through validated and scientific discoveries that are a part of its methodology.
A successful UX Methodology is primarily built on a detailed understanding of:
- Users and stakeholders of the business: Their demographics, potential, limitations, goals, and success.
- Nature of business and the environment it is conducted in: Devices, technology, physical location, and circumstances under which the system is used.
- Specific problems and challenges that the system intends to overcome: These could be anything from migrating legacy systems to reducing the number of clicks, fixing information architecture/navigation, or simply scaling consistently.
Benefits of Conducting Usability Testing
Conducting usability testing offers numerous benefits for product teams, designers, and organizations. By incorporating usability testing into the development process, teams can:
- Identify and Fix Usability Issues Early On: Usability testing helps uncover potential problems before they become costly to fix. For instance, identifying navigation issues in an enterprise application during the early design phase can save significant time and resources compared to addressing them post-launch.
- Improve Overall User Experience: A product that is easy to use and meets user expectations leads to higher user satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a healthcare app that allows doctors to quickly access patient records without hassle can significantly enhance their daily workflow and satisfaction.
- Enhance Accessibility: Usability testing ensures that products are accessible to a wider range of users, including those with disabilities. This inclusivity not only broadens the user base but also demonstrates a commitment to user-centric design.
- Gather Valuable Insights: Understanding user behavior and preferences through usability testing provides critical insights that inform design decisions. For instance, observing how users interact with a new feature can highlight areas for improvement that might not be evident through other research methods.
- Reduce Risk of Product Failure: By ensuring that a product meets user needs, usability testing minimizes the risk of launching a product that fails in the market. This proactive approach helps avoid wasted resources and potential revenue loss.
- Boost Market Competitiveness: A product that offers a superior user experience stands out in the market. Usability testing helps achieve this by refining the product to better meet user expectations compared to competitors.
- Increase Chances of a Successful Launch: Ensuring that a product is user-friendly and effective through usability testing increases the likelihood of a successful launch. This preparation helps build positive initial impressions and user adoption.
By conducting usability testing, teams can ensure that their product is user-friendly, efficient, and effective, ultimately leading to increased user satisfaction and business success.
Types of Usability Testing
Conducting usability testing offers numerous benefits for product teams, designers, and organizations. By incorporating usability testing into the development process, teams can:
- Identify and Fix Usability Issues Early On: Usability testing helps uncover potential problems before they become costly to fix. For instance, identifying navigation issues in an enterprise application during the early design phase can save significant time and resources compared to addressing them post-launch.
- Improve Overall User Experience: A product that is easy to use and meets user expectations leads to higher user satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a healthcare app that allows doctors to quickly access patient records without hassle can significantly enhance their daily workflow and satisfaction.
- Enhance Accessibility: Usability testing ensures that products are accessible to a wider range of users, including those with disabilities. This inclusivity not only broadens the user base but also demonstrates a commitment to user-centric design.
- Gather Valuable Insights: Understanding user behavior and preferences through usability testing provides critical insights that inform design decisions. For instance, observing how users interact with a new feature can highlight areas for improvement that might not be evident through other research methods.
- Reduce Risk of Product Failure: By ensuring that a product meets user needs, usability testing minimizes the risk of launching a product that fails in the market. This proactive approach helps avoid wasted resources and potential revenue loss.
- Boost Market Competitiveness: A product that offers a superior user experience stands out in the market. Usability testing helps achieve this by refining the product to better meet user expectations compared to competitors.
- Increase Chances of a Successful Launch: Ensuring that a product is user-friendly and effective through usability testing increases the likelihood of a successful launch. This preparation helps build positive initial impressions and user adoption.
By conducting usability testing, teams can ensure that their product is user-friendly, efficient, and effective, ultimately leading to increased user satisfaction and business success.
Types of Usability Testing
Types of enterprise application usability testing include:
- Moderated vs. Unmoderated Testing: Moderated involves a facilitator guiding the user, while unmoderated lets users complete tasks independently.
- Remote vs. In-Person Testing: Remote testing is conducted online, and in-person testing is conducted in a physical setting.
- Explorative Testing: Used in the early design phase to understand user behavior and needs.
- Assessment Testing: Conducted in the middle of the design process to evaluate the usability of specific features or the entire product.
- Comparative Testing: Compares two or more products or designs to determine which performs better in terms of usability.
Qualitative usability testing focuses on understanding users’ experiences, thoughts, and feelings through methods like think-aloud studies, observations, interviews, and surveys. In contrast, quantitative usability testing collects numerical data such as success rates and task completion times to identify patterns and generalize findings about the user experience.
What Is Usability Testing in Healthcare Technology?
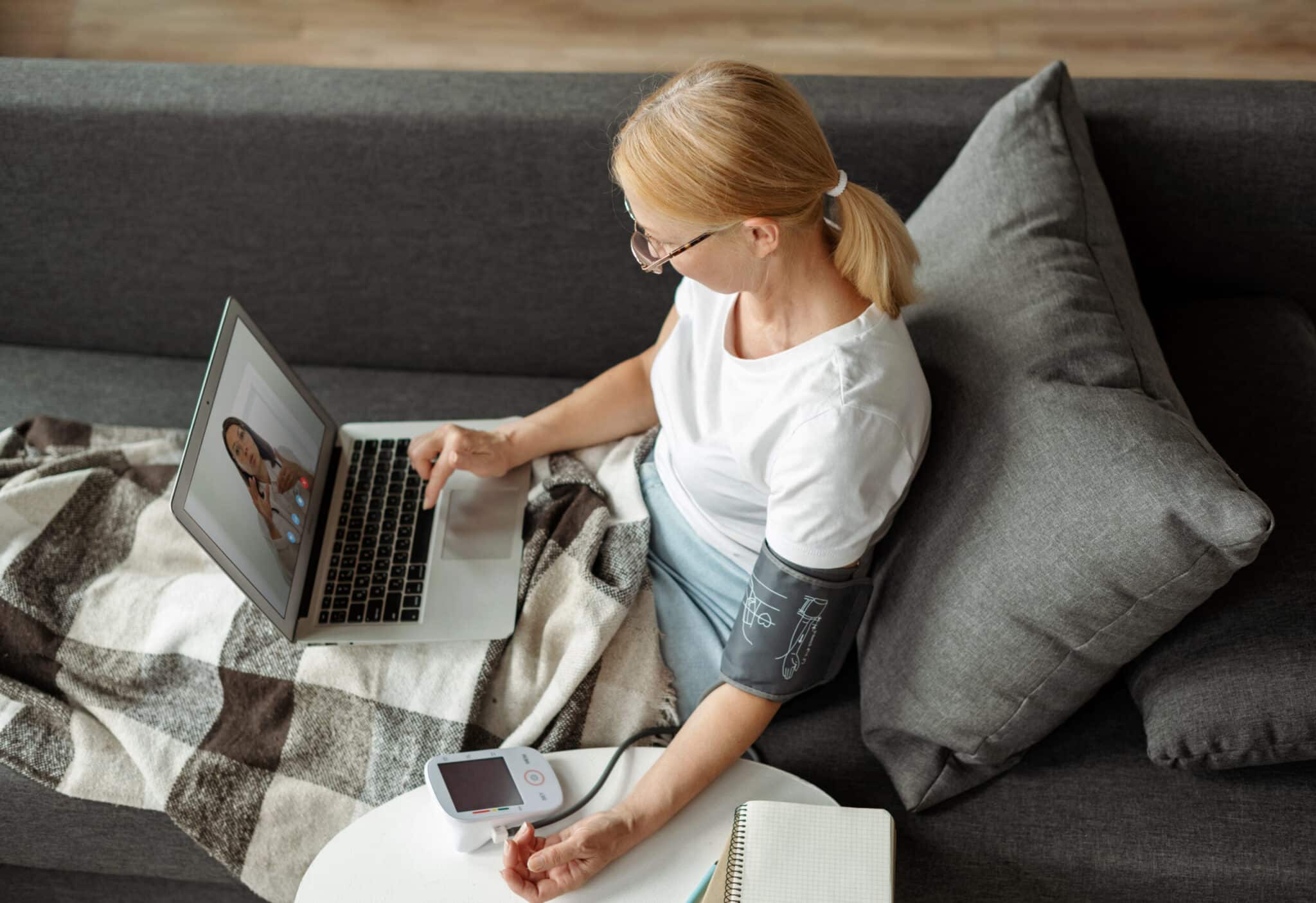

Usability testing in healthcare helps you analyze how effectively, efficiently, and satisfactorily healthcare professionals and patients can use medical software or equipment. Its importance lies in ensuring safety, improving healthcare quality, and enhancing user satisfaction.
For example, a well-designed Electronic Health Record (EHR) system with high usability allows doctors to input and retrieve patient information quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient care. This focus on usability is crucial in healthcare, where the stakes are high and even small usability issues can have significant consequences.
Remote Usability Testing Tools and Techniques
Remote usability testing has gained prominence with the shift to remote work, allowing for product testing across different locations. This method is essential in usability testing, especially when in-person testing is not feasible due to logistical or budget constraints.
What is Remote Usability Testing?
Remote usability testing is a method where users test a product or service in their own environment (such as home or office), while the researcher or moderator observes and gathers data from a different location.
This type of testing is especially useful for reaching a diverse group of users and for conducting tests when in-person meetings are not feasible, like in the context of social distancing. It allows for a more natural usage setting for the participant, providing authentic insights into the user experience. Remote usability testing can be either moderated, with real-time interaction between the user and researcher, or unmoderated, where users complete tasks independently.
Types of Remote Usability Testing Tools
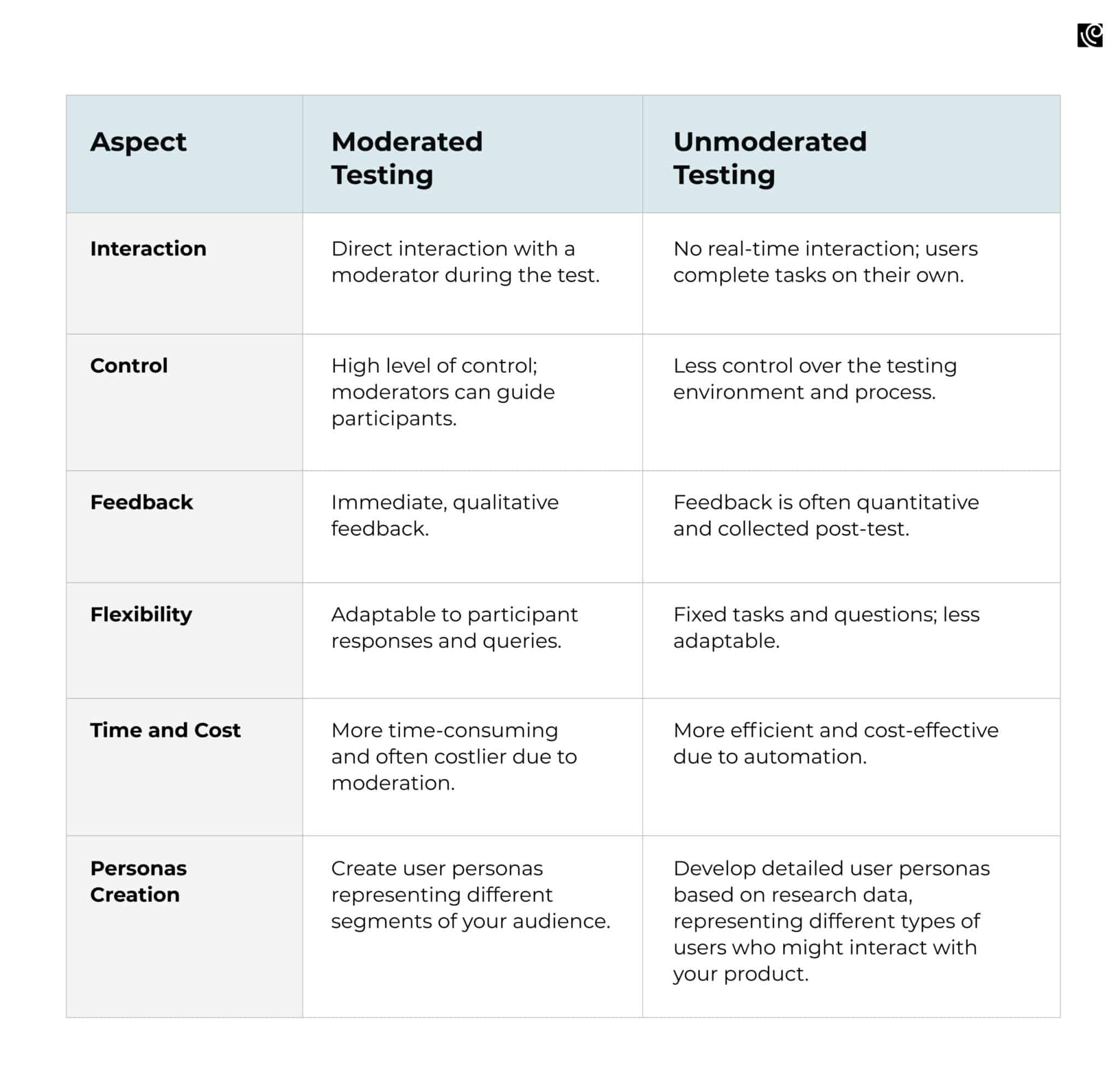
Remote usability testing comes in two forms: moderated and unmoderated. In moderated testing, a facilitator guides the participant through the test, often using video conferencing tools like Zoom or Google Meet.
This allows for real-time interaction and feedback. Unmoderated testing, on the other hand, involves participants completing tasks independently, with their sessions recorded for later review.
Moderated vs. Unmoderated Testing
7 Remote Usability Testing Tools that Suit Every Product and Budget

There are several tools available for remote usability testing, each with its unique features:
- UXArmy: Offers both qualitative and quantitative data through screen interaction videos, surveys, and visualizations.
- Usertesting.com: Known for its fast turnaround, this tool provides real user feedback through a video-first platform.
- UserZoom: Suitable for larger products, offering both moderated and unmoderated testing options.
- Optimal Workshop: Specializes in information architecture tests and offers a range of usability test types.
- Userlytics: Features a global panel and Picture-in-Picture system for detailed user insights.
- Maze: Focuses on quantitative usability metrics with seamless integration with design tools.
- UsabilityHub: A versatile platform offering various research tests with a large on-demand tester panel.
These tools are integral in understanding how real users respond to products, ensuring that designs are user-centric and effective. They underscore the mantra that “you are not your user,” highlighting the importance of external perspectives in design and product development.
Steps to Successful Usability Testing
User testing, encompassing various forms such as usability testing, product testing, and UX testing, is fundamental in creating products that are not only functional but also resonate with users. It’s a critical step in the design process, offering insights into how users interact with and perceive the design.
These insights can dramatically influence a product’s success and drive business profitability. However, it’s not uncommon for usability testing to reveal that a product is heading in the wrong direction, necessitating a restart. To prevent such scenarios, a well-structured approach to user testing is essential, ensuring valuable and timely feedback from real users.
Step 1: Planning and Goal Setting
Successful usability testing begins with clear planning and goal setting. Define specific objectives such as improving navigation or increasing conversion rates.
For example, in enterprise software design, the goal might be to streamline the workflow for efficiency. This phase involves outlining the scope, methodology, and success metrics, ensuring alignment with business objectives and user needs.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Users
Choose participants who represent your target audience. In healthcare usability, this might mean selecting healthcare professionals and patients to test a new clinical information system, ensuring the feedback is relevant and actionable.
Step 3: Conducting the Test
Implement the test according to the plan. For instance, in an enterprise application, you might ask users to complete tasks while observing their interactions.
This step involves collecting data on user behavior and preferences, which is vital for refining the product. Use tools and techniques suited to your test type, whether moderated or unmoderated, remote or in-person.
Step 4: Analyzing and Reporting Test Results
Analyzing and reporting test results is a critical step in the usability testing process. The goal of analysis is to identify usability issues, patterns, and trends, and to provide recommendations for improvement.
To analyze test results, teams can use a variety of methods, including:
- Quantitative Analysis: This involves analyzing numerical data, such as completion rates, error rates, and time-on-task, to identify trends and patterns. For example, if a significant number of users struggle to complete a specific task, it indicates a usability issue that needs addressing.
- Qualitative Analysis: This involves analyzing non-numerical data, such as user feedback, comments, and observations, to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior and preferences. For instance, user comments about confusing navigation can provide insights into specific areas that need redesign.
- Thematic Analysis: This involves identifying and coding themes and patterns in the data to pinpoint common issues and areas for improvement. For example, recurring themes about difficulties in finding certain features can highlight the need for better information architecture.
When reporting test results, teams should:
- Provide a Clear and Concise Summary: Highlight the most critical usability issues and recommendations for improvement. This summary should be easily digestible for stakeholders who may not have time to delve into detailed reports.
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporate graphs, charts, and diagrams to illustrate findings. Visual aids make the report more engaging and help convey complex data more effectively.
- Include User Quotes and Feedback: Providing direct quotes from users adds context and illustrates the real-world impact of usability issues. This qualitative data can be powerful in driving home the importance of certain changes.
- Offer Actionable Recommendations: Provide specific design changes and usability fixes. For example, if users find a particular feature hard to locate, recommend changes to the navigation structure or interface design.
- Include an Implementation Plan: Outline a plan for implementing the recommended changes, including timelines and resource allocation. This ensures that the findings lead to actionable steps and improvements.
By analyzing and reporting test results effectively, teams can ensure that usability testing has a meaningful impact on the product development process, and that usability issues are addressed in a timely and effective manner.
Challenges in Enterprise Usability Testing
- Complex User Requirements: Enterprise systems often have a diverse user base, each with different needs and skill levels. For instance, CRM software used by both sales and marketing teams might struggle to balance simplicity for new users with advanced features for experienced users. This diversity can make it challenging to design a universally intuitive interface.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many enterprises rely on legacy systems, and new software must often integrate with these older systems. This integration can limit design flexibility and enterprise user experience. For example, integrating a modern HR platform with an outdated payroll system might lead to cumbersome workflows and reduced efficiency.
- High Stakes and Security Concerns: Enterprise applications frequently handle sensitive data, where usability issues can lead to significant security risks. An example is a financial reporting tool that needs to be both user-friendly and highly secure, a balance that is challenging to achieve.
- Scalability and Performance: Enterprise systems must be scalable and perform well under heavy use. Usability testing must, therefore, account for performance under load. For instance, an e-commerce platform experiencing slow load times during peak usage hours can lead to a poor user experience.
- Aligning with Business Processes: The biggest challenge is aligning the system’s usability with existing business processes. For example, a project management tool needs to adapt to the company’s project methodologies, which can vary greatly and may require significant customization in the software.
Usability Testing Challenges in Healthcare
Most usability problems in healthcare are due to the critical nature of healthcare applications. Let’s look at these challenges in detail:
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring user data protection while maintaining usability is a major challenge. For instance, electronic health record systems must secure patient data, which can complicate access and usability.
- Complex User Interfaces: Healthcare software often has complex interfaces to accommodate vast medical data, which can overwhelm users. For example, a radiology imaging system with a cluttered interface can hinder efficient usage by radiologists.
- Adapting to Varied User Skill Levels: Healthcare tools are used by a wide range of professionals, from nurses to specialists, each with different expertise levels. An application that’s too technical can be challenging for less tech-savvy staff.
- Integrating with Existing Systems: Healthcare software must often integrate with various existing systems, which can be technically challenging and affect user experience. For example, integrating a new patient management system with an older billing system can result in a disjointed experience.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare applications must comply with numerous regulations, which can restrict design flexibility. For example, meeting FDA requirements for a medical device app can limit innovative UX solutions.
Essential Strategies for Effective Usability Testing

In the realm of usability testing, adopting the right strategies is crucial for garnering valuable insights and enhancing product design. Let’s explore the key practices that can significantly improve the effectiveness of usability testing processes:
- Focusing on End-User Needs and Preferences: In user-centered design, understanding and prioritizing the end-user’s requirements is key. For example, in healthcare apps, input from doctors and patients during the design process can ensure the app addresses their specific needs, enhancing usability and effectiveness.
- Implementing Iterative Testing and Feedback: This approach involves continuously testing and refining the product based on user feedback. In the context of enterprise applications, it might mean conducting regular usability sessions with a diverse group of users to iteratively refine features, thereby ensuring the application evolves in line with user expectations and requirements.
- Simplifying Navigation for User Efficiency: Easy and intuitive navigation is crucial, especially in complex systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP). Simplifying the dashboard in an ERP system enhances user efficiency by allowing quick access to essential functions and information.
- Ensuring Accessibility and Inclusivity: Accessibility in application design ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can effectively use the software. For instance, incorporating voice commands in healthcare software can significantly aid visually impaired users, making the application more inclusive.
- Maintaining Consistent User Interface (UI): Consistency in the user interface helps in reducing the learning curve for users. Using uniform color schemes and button styles throughout an enterprise application, for example, can help users navigate more confidently and efficiently.
- Optimizing Performance for Responsiveness: Prioritizing software performance to ensure it is responsive and loads quickly is essential. In healthcare, optimizing the loading times of patient records can be crucial, allowing medical staff to access vital information swiftly, thereby improving care delivery efficiency.
- Updating Regularly Based on User Feedback: Continual improvement based on user feedback helps keep the application relevant and user-friendly. In an enterprise environment, this may include adding new features or adjusting existing ones to align with employee feedback and evolving usage patterns.
- Managing Information Presentation to Avoid Overload: Presenting information in an organized, digestible manner is critical, especially in fields like healthcare where decision-making is data-driven. This involves highlighting key patient information prominently, while making less critical data accessible but not immediately visible, thus preventing information overload.
Integrating Usability Testing into Your Development Process
Integrating usability testing into the development process is essential for ensuring that products meet user needs and expectations. Here are some tips for integrating usability testing into your development process:
- Conduct Usability Testing Early and Often: Usability testing should be conducted throughout the development process, from the early stages of product design to the final stages of testing and launch. Early testing helps catch issues before they become ingrained in the design, while ongoing testing ensures continuous improvement.
- Make Usability Testing a Part of Your Agile Development Process: Usability testing can be incorporated into agile development methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, to ensure that user feedback is continuously integrated. For example, conducting usability tests at the end of each sprint can provide timely insights that inform the next iteration.
- Use Usability Testing to Inform Design Decisions: Rather than using usability testing solely to validate existing designs, leverage it to inform design decisions from the outset. This proactive approach ensures that user needs are considered throughout the design process.
- Involve Stakeholders in the Usability Testing Process: Engage product managers, designers, and developers in the usability testing process. This involvement ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and aware of usability issues and recommendations for improvement.
- Use Remote Usability Testing to Reach a Wider Audience: Remote usability testing allows you to gather feedback from users in different locations and time zones. This broader reach can provide more diverse insights and ensure that the product meets the needs of a global user base.
- Measure the Effectiveness of Design Changes: Use usability testing to measure the impact of design changes. For example, after implementing a new feature, conduct usability tests to ensure it meets user needs and resolves previous issues.
By integrating usability testing into the development process, teams can ensure that products meet user needs and expectations, and that usability issues are addressed in a timely and effective manner. This approach not only enhances the user experience but also contributes to the overall success and competitiveness of the product.
In conclusion
The future of usability testing in enterprise and healthcare is integral to continuous improvement and adaptation. Understanding and implementing usability in healthcare is not just about enhancing user interaction; it plays a crucial role in patient care and healthcare delivery.
The purpose of usability testing in these sectors is to constantly evolve with technological advancements and user needs, ensuring that software and applications are not only efficient but also user-friendly and inclusive. As technology continues to advance, the role of usability testing will become increasingly vital in shaping user-centric designs that cater to the complex and dynamic nature of enterprise and healthcare environments.
At Koru, we take usability testing with utmost seriousness, recognizing its critical role in shaping enterprise and healthcare software. Our team of enterprise usability experts is adept at employing advanced enterprise usability testing tools to ensure that every aspect of the user experience is meticulously examined and optimized. We understand the nuances of healthcare software usability and are committed to providing comprehensive usability test guides. Our approach to enterprise usability testing is not just about finding issues but about continuous improvement, ensuring that our solutions are not only functional but also intuitive and user-friendly.









