-
Design Thinking
Radical EHR Solution That Humanizes Patient-Provider Interactions
Background
“There is nothing more frustrating to a patient than talking to their doctor, wanting advice, and that provider is typing away and looking at a computer screen instead of the patient. That most fundamental aspect of human communication, which is eye contact, now is being robbed from the medical encounter because of the electronic health record.”
Dr. Lloyd Minor, Dean, Stanford University School of Medicine
Physicians see EHRs as storage—not clinical—tools; about half say it detracts from their clinical effectiveness.*
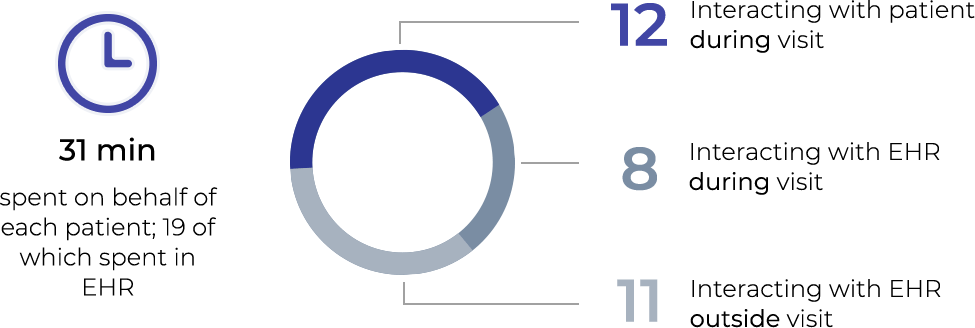
Problem Statement
For Doctors
Rather than focusing on the interaction with the patient, healthcare providers are involuntarily thinking of what needs to be documented or navigating the complex EHR.
For patients
With the doctors preoccupied with navigating the complex EHR, patients have to suffer. Half-hearted participation from the doctor caused an unsatisfactory interaction for the patient.
There lies a pressing need to upgrade the existing system for healthcare providers and practices to improve their relationships with patients and deliver top-notch services.
Our client is a global leader in healthcare IT, delivering quality care and industry-leading practice management solutions to 130,000 doctors and nurses and 850,000 medical professionals.
Goal
Create an EHR snapshot of the patient’s clinical details to enable the provider (user) to view the most important aspects of the patient’s health history in order to make the right diagnosis for the patient’s current visit.
UX Strategy
At Koru, our design process is focused on improving the usability, accessibility, and delight provided in product interaction. Keeping the user in the center of the creative process leads us to create designs that are clutter-free, easy, intuitive, scalable, engaging, and provide a fabulous experience to the users.
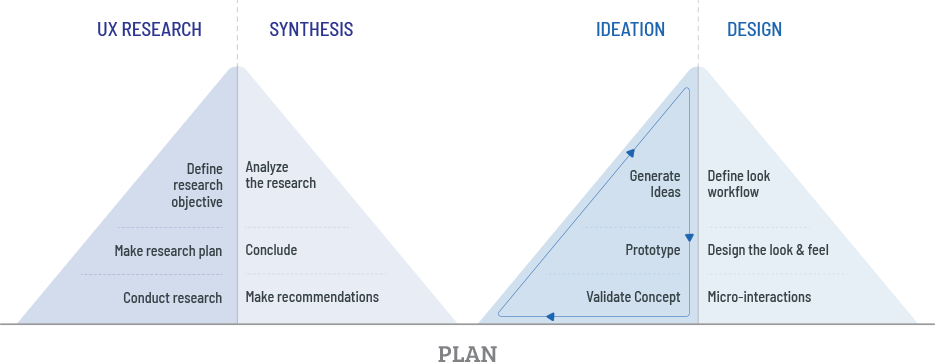
Process
Research
- Understand and review data that a provider would refer to for a patient during the visit
- Review the visit process from the provider’s perspective
- Review and study documentation generated post appointments
Synthesis
- Journey map for office/virtual visits
- Clinical information referred to by the physician
- Actions that a provider could take
- Prescribe medication
- Prescribe lab/diagnosis
- Refer to another doctor
- Set a followup appointment
- Change the parent diagnosis
User Journey For Office Visits

Key Findings
- Information randomly distributed across the EHR
- Information is not displayed as per the context
- Providers preoccupied with navigating the complex interface
- Multiple keystrokes and screens to fulfill a basic search query
- Long scroll to navigate and arrive at the necessary information
- Documentation is a tedious process
- Quality of documentation suffers as doctors are hard-pressed for time
- Doctors are prone to skip certain details while documenting at the end of an appointment
- Unawares, doctors tend to feed incomplete or vague details/instructions for their support staff
Design Brief – Key Focus Areas
Our objective was to create a simplified snapshot of the patient’s vital details so as to enable the provider to process it in a short time and complete his intended action. We had to ensure that the provider be more focused on the interaction with the patient, rather than be distracted by the overwhelming EHR usage.
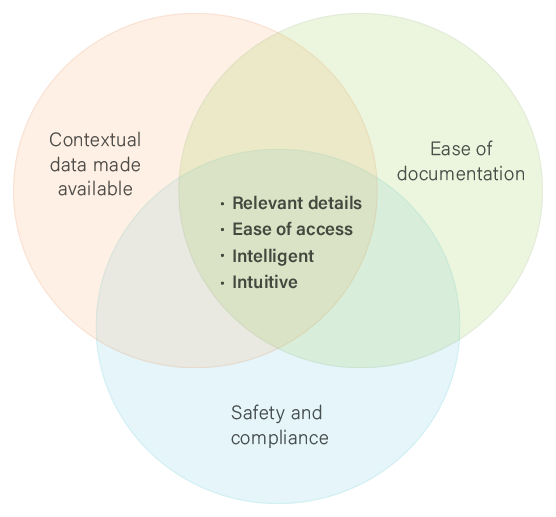
The idea was to create an EHR tool that’s actually a source of assistance instead of being a source of intimidation.
All the while, we had to ensure that patient safety and compliance standards were fulfilled.
Ideation
We made multiple variations that were tested with the users. We wanted to evaluate the prototypes on the following-
- Information – Is it contextual and relevant?
- Navigation – Is it intuitive and discoverable?
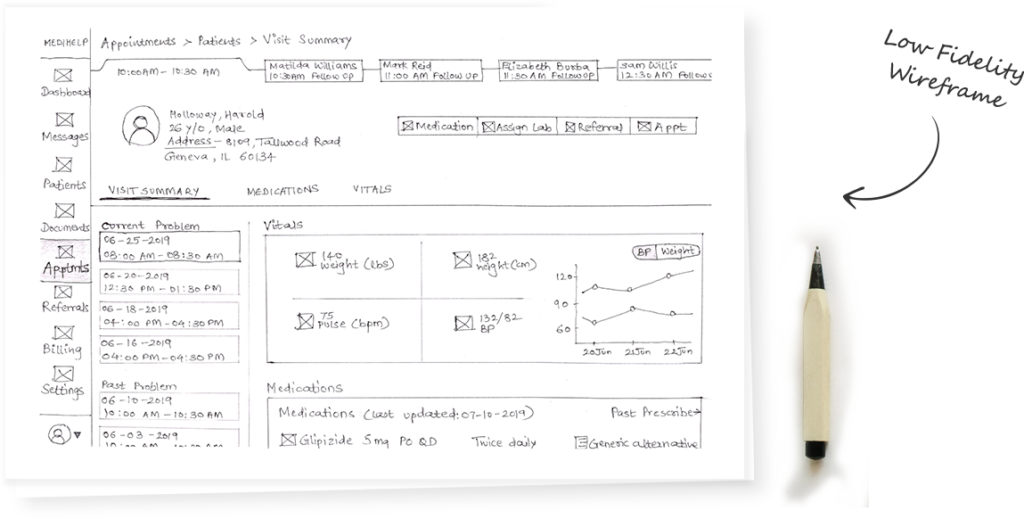
Design
The process of validating the solution begins with transforming the wireframes and prototypes into actual images with themes, components and styles applied to them.
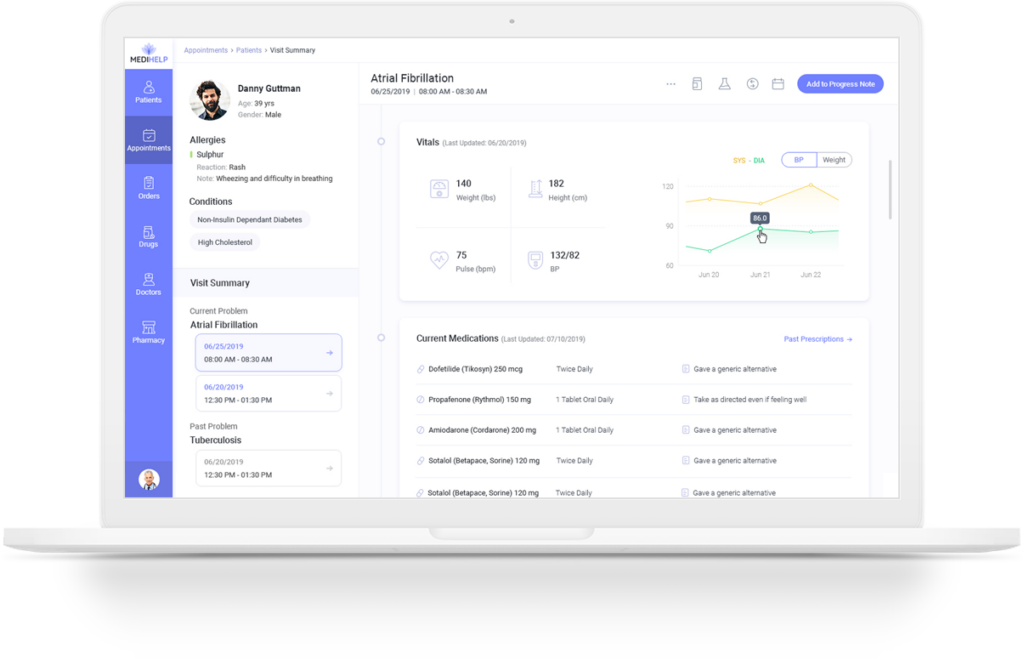
Highlights
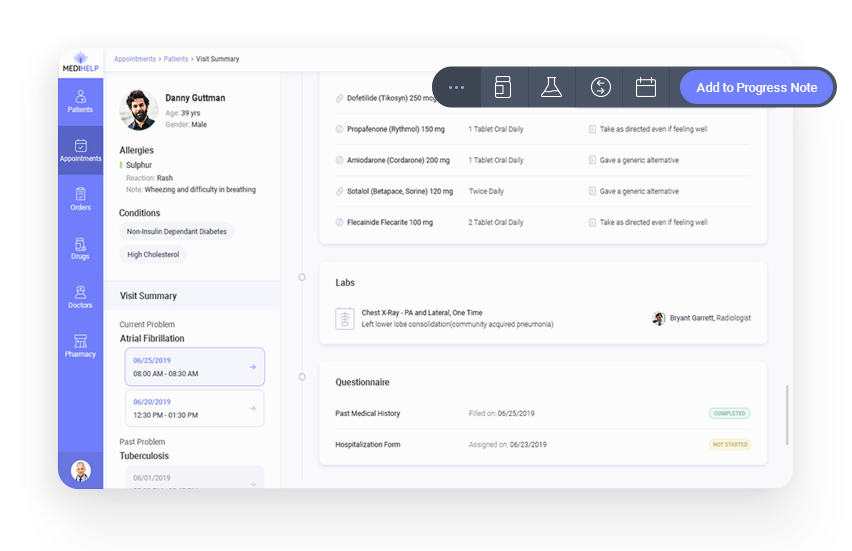
- Floating toolbar is visible through the scroll, and gives continued access to editing
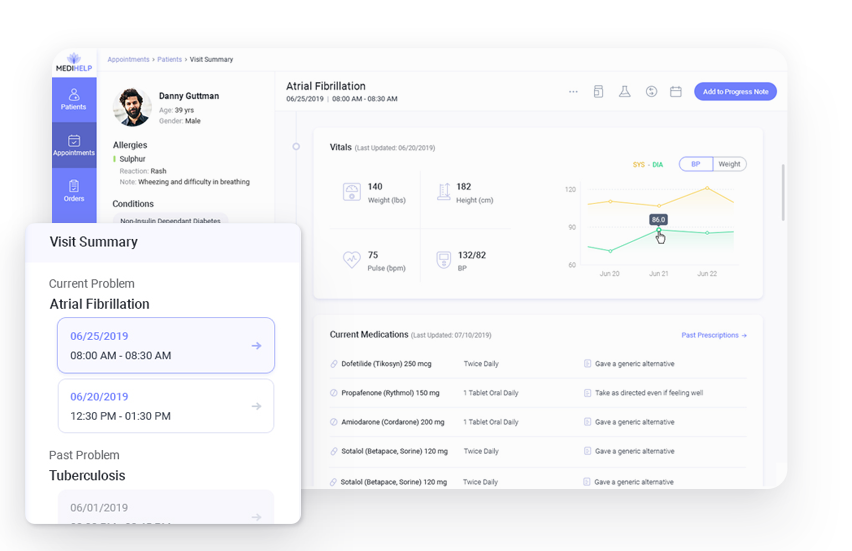
- Easy visibility of context of the patient’s current visit
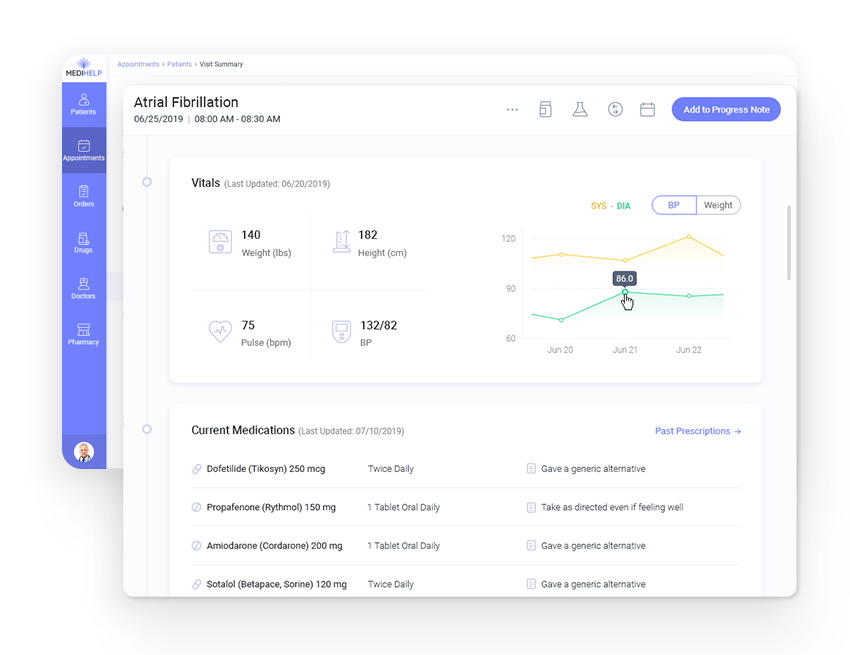
- All the important and relevant details are available at a glance
- Dictation tool records the conversation and lets the doctor proceed with the discussion without having to worry about documenting
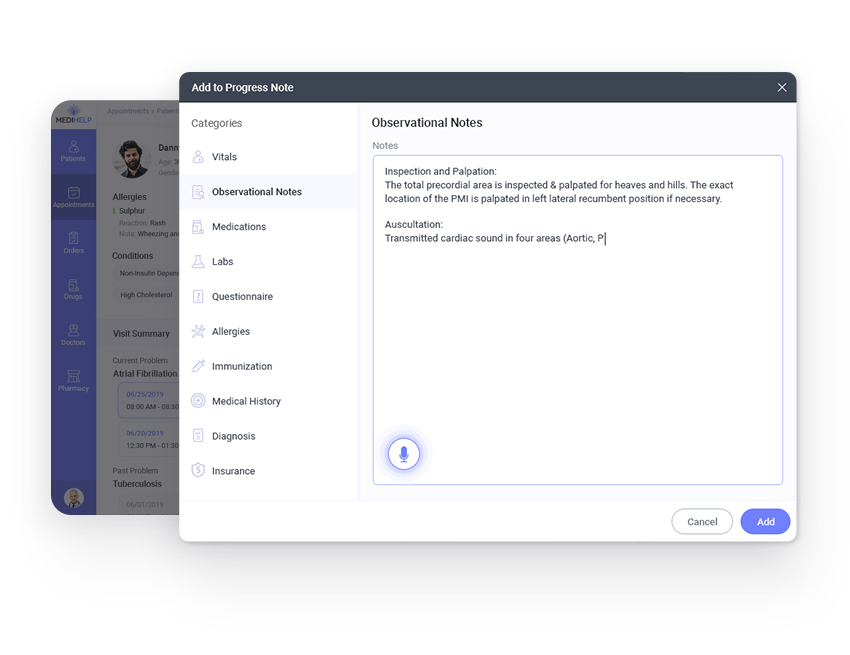
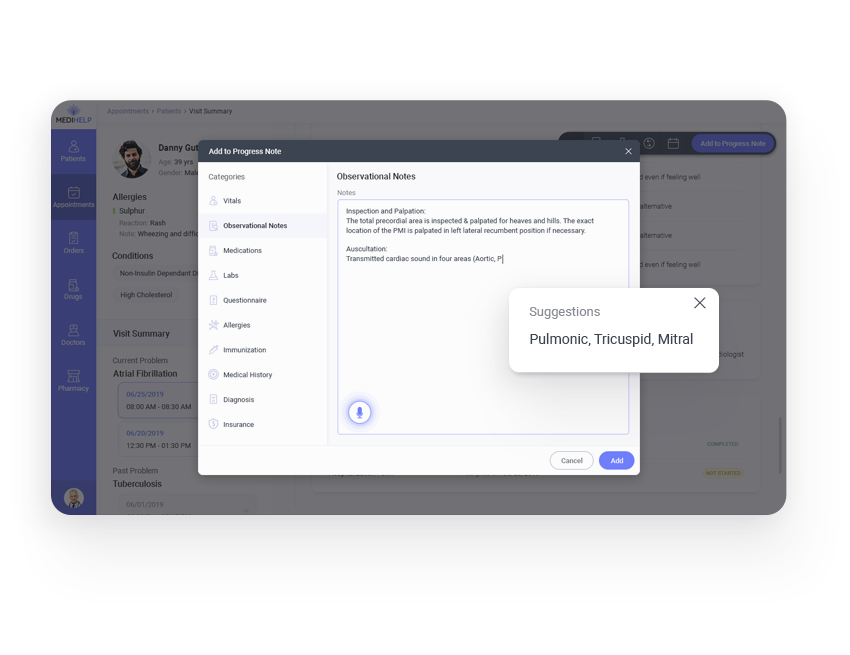
- Suggested codes during documentation speed up data entry and reduce erroneous entries
Impact
The EHR system was implemented to create efficiencies in workflow, providing accurate, updated, and complete information about patients at the point of care.
Quick access to patient records enabled more coordinated, efficient care and improved clinical decision-making by 24%.
“An intelligent EHR system is a crucial tool that helps us be proactive and attentive during a patient interaction. With a simple and easy-to-navigate EHR such as this, I am better able to inform patients about trends in their personal data, and provide evidence-based medical care.”
Dr. Andy Wilkins
Ready to make a difference with design?
Let’s talk about the infinite possibilities of a design thinking approach!